Understanding the Differences Between Air-Driven & Electric Dental Handpieces
Behind every great dentist is a great dental handpiece. But as most dentists know, handpieces require a diligent maintenance routine and are prone to break down. The first step in preventing damage to your dental handpiece is gaining an in-depth understanding of how your handpiece operates. Read on to learn more about the history of dental handpieces and the difference between air-driven and electric handpieces. We’ll also let you know how First Choice Repair can help you maintain your handpiece for years to come.
The History of the Dental Handpiece
If you were a dentist in America prior to 1950, you were probably using an electric belt-driven instrument that topped out at a speed of 50,000 RPM. The low rotational speed meant that procedures took longer and were more painful for the patient. There was also the problem of instruments being bulky. They even occasionally got tangled in the hair of whoever was unlucky enough to be nearby. Clearly, a change was needed.
In 1949, Sir John Patrick Walsh of New Zealand received a patent for an air-driven handpiece that would soon revolutionize the industry. By 1957, Dr. John Borden had developed the product in America and it was being manufactured by the DENTSPLY company and distributed with the name Borden Airotor. The “restorative dentistry” that we are so familiar with today was made possible by the increased speed and precision of this new dental technology.
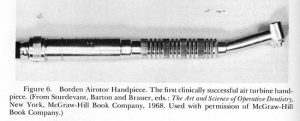
Since the mid-20th century, advancements have been made in both air-driven and electric dental handpieces that allow for easier use by dentists and a more comfortable experience for the patient. Understanding the differences between the two will help you make the right choice for your practice.
Comparing Air-Driven vs. Electric Handpieces
There are advantages and disadvantages to using both electric and air-driven dental handpieces, which we’ll discuss here:
| Electric Dental Handpieces | Air-Driven Dental Handpieces |
|---|---|
| Electric handpieces use a simple electrical supply to power the motor. | High-speed air-driven handpieces use a turbine to rotate the rotary cutting instrument. |
| They can function from 20 RPM up to 200,000 RPM. | Air-driven high-speed handpieces can function at up to 400,000 RPM, but usually operate between 180,000 to 330,000 RPM. |
| Because it’s possible to use different speeds, there is more room for versatility. They can be used for high speed and low speed procedures. | High speeds lead to faster cutting and reduced procedure time. |
| The head of the handpiece can become hot and there have been cases of patient burns. | With more intense procedures, the bur can slow, decreasing cutting performance. |
| The constant torque results in a better cutting performance. | Changes in design to increase torque speed resulted in increased turbine and head size. |
The overall functionality of modern dental handpieces had not changed much until a few years ago. Now, technological developments are allowing for more precision and lighter handpieces. First Choice Repair has a variety of handpieces available for purchase. We are happy to answer your questions to ensure that you get the dental handpiece that works for your needs.
Of course, with any kind of dental handpiece, regular maintenance is critical to ensure longevity. Check out any of these blogs for great tips on how to maintain your handpiece and diagnose any problems:
- 3 Symptoms Your Dental Handpiece Isn’t Working Properly
- Maintaining Your Dental Handpieces
- 3 Tips To Improve The Performance Of Your Dental Handpieces
If you run into any problems with your electric OR air-driven handpieces, First Choice Repair has 25 years of experience that can help solve your problem. Just contact us, we’d love to help.
1.800.569.6627